I get commissions for purchases made through links on the site. As an Amazon and Clickbank Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. Learn more.
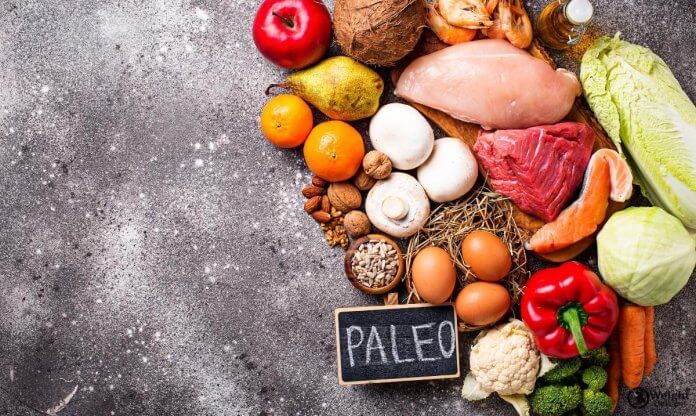
The Paleo diet, often known as the caveman diet, is more than just a weight loss trend; it’s a return to the eating habits of our ancestors. Rooted in the Paleolithic era, this diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, replicating the way hunter-gatherers ate thousands of years ago. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of the Paleo diet, its health benefits, practical tips for adoption, and answer some common questions to help you decide if it’s the right choice for your lifestyle.
Table of contents
Key Takeaways
- Back to Basics: The Paleo diet focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed foods similar to what our Paleolithic ancestors ate.
- Weight Management: It naturally promotes weight loss and better body composition due to reduced calorie intake and high protein content.
- Reduced Processed Foods: By eliminating processed foods, refined sugars, and grains, the diet contributes to overall better health.
- Balanced Blood Sugar: Lower carbohydrate intake and elimination of refined sugars help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Gut Health Improvement: The diet’s emphasis on fiber-rich vegetables and exclusion of processed foods enhances gut health.
- Anti-inflammatory Benefits: Paleo’s focus on anti-inflammatory foods helps reduce chronic inflammation, a key to overall health.
- Nutrient-Rich Diet: It ensures a diet high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants due to the emphasis on fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and nuts.
- Lifestyle Change, Not a Fad: The Paleo diet is a long-term lifestyle choice encouraging mindful eating and overall wellbeing, not just a quick weight loss fix.
- Customization is Key: It’s important to adapt the diet to individual nutritional needs and lifestyle preferences, possibly with professional advice.
- Holistic Health Approach: The Paleo diet supports a holistic approach to health, focusing on food quality and the relationship between diet and health.
Understanding the Paleo Diet
The Paleo diet revolves around a simple premise: if your Paleolithic ancestors didn’t eat it, neither should you. This means focusing on foods that could be hunted or gathered, such as meats, fish, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables. The diet excludes agricultural and processed foods like grains, dairy, legumes, and refined sugars.
Historically, our ancestors’ diets varied significantly based on geography and seasonality, but they shared a common trait: they were natural and unprocessed. Proponents of the Paleo diet argue that the human body is genetically mismatched to the modern diet that emerged with farming practices — an idea known as the “discordance hypothesis.” They suggest that it is this mismatch that contributes to the prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease today.
Benefits of the Paleo Diet
Embarking on the Paleo diet can bring numerous health benefits, aligning with the belief that eating more like our ancient ancestors can lead to a healthier lifestyle. Here are some of the key benefits associated with following a Paleo diet:
- Weight Loss and Improved Body Composition: Many people turn to the Paleo diet for weight loss. By eliminating processed foods, refined sugars, and grains, the diet naturally reduces calorie intake and promotes a healthier body composition. The emphasis on protein-rich foods also helps in feeling fuller for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
- Stabilized Blood Sugar Levels: The Paleo diet, being low in carbohydrates compared to typical Western diets, can help stabilize blood sugar levels. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes. The diet’s focus on high-fiber fruits and vegetables also aids in this regard.
- Improved Gut Health: The exclusion of processed foods and grains, which can be inflammatory for some people, can lead to better gut health. Many people report a reduction in bloating, gas, and other digestive issues after switching to a Paleo diet.
- Increased Energy and Better Sleep: Adopting a Paleo diet can lead to more stable energy levels throughout the day. This is partly due to the steady blood sugar levels and partly due to the high-quality nutrients consumed. Additionally, the diet’s natural, unprocessed foods can contribute to better sleep patterns.
- Reduced Inflammation and Enhanced Immune Function: The Paleo diet is rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as leafy greens, fatty fish, and nuts. These foods can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to a range of chronic diseases. Moreover, the diet’s emphasis on whole foods ensures a good intake of antioxidants, which can bolster the immune system.
- Improved Heart Health: By focusing on lean meats, healthy fats, and fresh produce, the Paleo diet can have a positive impact on heart health. It promotes a healthier balance of cholesterol and reduces the risk of heart disease.
- Enhanced Mental Clarity and Mood Stability: The balance of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates in the Paleo diet can contribute to better brain health. Nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and certain nuts and seeds, are known to enhance cognitive function and mood.
- Support for Healthy Skin and Hair: The natural, nutrient-dense foods in the Paleo diet can have a beneficial impact on skin and hair health. Vitamins and minerals from fresh fruits and vegetables, along with healthy fats, contribute to a glowing complexion and strong hair.
What to Eat on the Paleo Diet
The Paleo diet emphasizes eating whole, nutrient-dense foods that were available to our Paleolithic ancestors. Here is a list of foods that are typically included in a Paleo diet:
- Meats: Grass-fed, pasture-raised, and wild meats are preferred. This includes beef, lamb, pork, poultry, and game meats. These sources are richer in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and are free from antibiotics and hormones often found in conventionally raised meat.
- Fish and Seafood: Wild-caught fish and seafood are recommended. Salmon, mackerel, trout, haddock, shrimp, and shellfish are great choices, being high in protein and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Eggs: Eggs are a staple in the Paleo diet, providing a good source of protein and nutrients. Free-range or omega-3 enriched eggs are the best options.
- Vegetables: Almost all vegetables are Paleo-friendly. Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, peppers, onions, carrots, and tomatoes are just a few examples. These are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Fruits: Fruits are a natural source of sweetness in the Paleo diet. Berries, apples, bananas, oranges, pears, and grapes are all good choices. However, those watching their sugar intake may need to moderate fruit consumption.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds are great for snacking or as additions to meals. They provide healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Healthy Fats and Oils: Olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil, and ghee (clarified butter) are good fat sources. These oils are less processed and have a better nutrient profile compared to refined vegetable oils.
- Tubers: Sweet potatoes, yams, and other root vegetables are excellent sources of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Herbs and Spices: Fresh and dried herbs and spices are used to flavor Paleo meals. This includes garlic, turmeric, rosemary, thyme, and cinnamon, among others.
- Drinks: Water is the primary beverage on the Paleo diet. Herbal teas and bone broth are also Paleo-friendly.
The Paleo diet focuses on whole foods and eliminates processed foods, grains, legumes, and dairy. It’s not just about what you eat but also the quality of the foods. Opting for organic, grass-fed, and wild-caught options whenever possible ensures a higher nutrient content and reduces exposure to additives and chemicals. This diet encourages a varied and balanced intake of natural foods, which can lead to an overall healthier lifestyle.
Paleo Diet Impact on Weight Loss
The Paleo diet has gained popularity partly due to its potential impact on weight loss. Here’s how following a Paleo dietary approach can contribute to shedding pounds:
- Natural Calorie Reduction: The Paleo diet eliminates processed foods, which are often high in calories and low in nutrients. By focusing on whole foods like lean meats, vegetables, and nuts, you naturally consume fewer calories while still feeling satiated, leading to weight loss.
- High Protein Intake: Protein is a key component of the Paleo diet. Consuming a diet high in protein can increase satiety, reduce hunger, and boost metabolic rate. This helps in muscle building and maintenance, which is crucial for burning more calories, even at rest.
- Low Carb Profile: Although not a low-carb diet per se, the Paleo diet tends to be lower in carbs than typical Western diets because it excludes grains and processed sugars. This reduction in carb intake can lead to decreased insulin levels and fat storage, encouraging the body to burn stored fat for energy.
- Better Blood Sugar Regulation: The Paleo diet’s emphasis on low-glycemic fruits and vegetables, along with the absence of refined sugars, aids in stabilizing blood sugar levels. This can be particularly beneficial for weight management and reducing cravings for unhealthy foods.
- Improved Gut Health: The focus on fiber-rich vegetables and fruits, along with the exclusion of processed foods, can improve gut health. A healthier gut is linked to better digestion and metabolism, which can aid in weight loss.
- Reduction in Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can be a barrier to weight loss. The Paleo diet’s anti-inflammatory nature, due to its high intake of antioxidants and healthy fats, can help reduce inflammation, potentially easing the weight loss process.
- Elimination of Empty Calories: By cutting out processed foods, sodas, and refined sugars, the Paleo diet ensures that almost every calorie consumed is nutrient-dense. This can lead to a natural decrease in overall calorie intake and aid in weight loss.
- Sustainable Eating Habits: The Paleo diet promotes a long-term healthy eating approach rather than a quick-fix diet. This sustainability can lead to more consistent and lasting weight loss.
- Increased Physical Activity Encouragement: The Paleo lifestyle often includes recommendations for increased physical activity, mimicking the active lifestyle of Paleolithic humans. This exercise component can further contribute to weight loss and overall health.
In summary, the Paleo diet can be an effective tool for weight loss due to its focus on whole, unprocessed foods, high protein and fiber content, and a balanced approach to nutrition. As with any diet, individual results may vary, and it’s important to consider personal health needs and consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
Conclusion
In essence, the Paleo diet is more than a dietary trend; it’s a return to the basics of eating whole, unprocessed foods. This approach not only supports effective weight management but also promotes overall health improvements, including enhanced gut health, reduced inflammation, and better nutrient balance. While it may not be ideal for everyone, its principles of minimizing processed foods and sugars can benefit all. As a lifestyle choice, the Paleo diet encourages a holistic understanding of food and its impact on health. Tailoring it to individual needs and preferences, possibly with professional guidance, can unlock a healthier and more vibrant way of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Paleo Diet is a nutritional approach that mimics the eating habits of our Paleolithic ancestors. It focuses on consuming whole foods like lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, and excludes processed foods, grains, legumes, and dairy.
Yes, many people find that they lose weight on the Paleo Diet. This is often due to its emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods, which typically leads to a reduction in calorie intake and an increase in nutrient-dense foods that promote satiety and metabolic health.
While the Paleo Diet can be healthy, it’s not suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain health conditions, pregnant women, and children may need to modify the diet or seek alternative diets. It’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new diet, especially one that involves significant dietary changes.
On the Paleo Diet, you should avoid processed foods, grains (like wheat, oats, and barley), legumes (such as beans, lentils, peanuts), dairy products, refined sugar, and artificial sweeteners. The focus is on eating foods in their most natural form.
The Paleo Diet differs from the Keto Diet in its carbohydrate allowance; Paleo does not necessarily restrict carbs but focuses on the source of the carbs. Compared to a Vegan diet, Paleo includes meat and fish, focusing on high-quality, sustainably sourced animal products, whereas Veganism excludes all animal-derived products.